Definition
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble antioxidant vital for immune defense, collagen synthesis, and cellular repair. Unlike most animals, humans cannot synthesize Vitamin C — it must be obtained entirely through diet.
Beyond its classic association with preventing scurvy, Vitamin C functions as a powerful electron donor, neutralizing free radicals and regenerating other antioxidants like Vitamin E. It is one of the most crucial vitamins for maintaining tissue integrity and resilience under physiological stress.
Where It’s Found
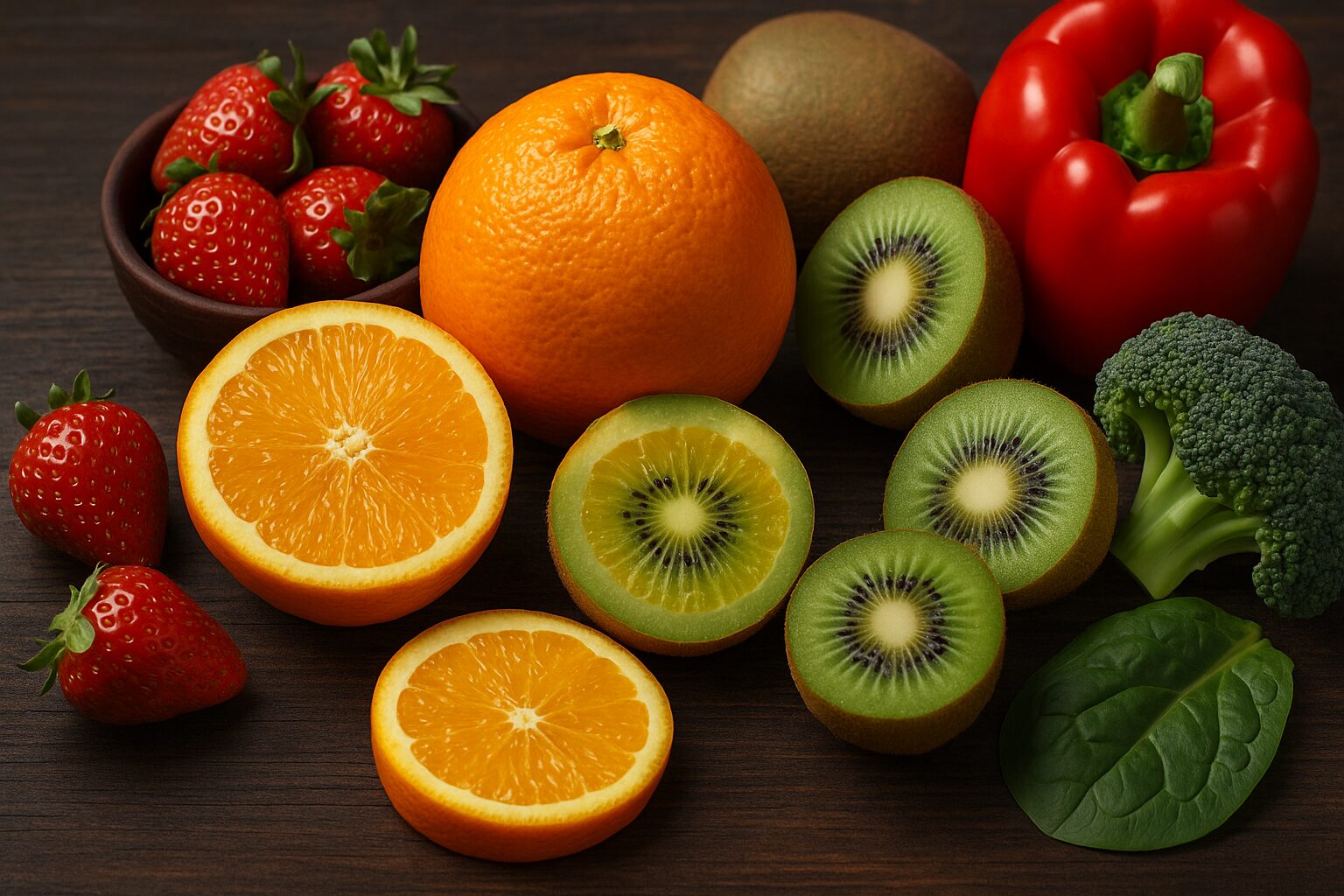
Vitamin C is abundant in a wide variety of plant-based foods. Top sources include citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes), kiwi, strawberries, papaya, bell peppers, broccoli, and kale.
Because it is sensitive to heat and oxygen, prolonged cooking or storage significantly reduces Vitamin C content. Eating these foods fresh or lightly cooked helps preserve their potency. Modern diets rich in processed foods are often deficient in Vitamin C despite apparent caloric abundance.
Function in the Human Body
Vitamin C is best known for its role in collagen production — the structural protein that forms connective tissues, tendons, ligaments, and skin. It acts as a cofactor in the hydroxylation of proline and lysine, stabilizing collagen fibers and enabling tissue repair.
It is also essential for immune function. Vitamin C enhances white blood cell activity, promotes the production of interferons, and reduces inflammatory cytokines. During infection or stress, the body’s Vitamin C levels drop sharply, showing how directly it supports defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, Vitamin C improves iron absorption, accelerates wound healing, and aids in the synthesis of carnitine — a molecule that transports fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. In short, it connects immunity, recovery, and metabolism at a cellular level.
Relationship with Physical Performance
For athletes and physically active individuals, Vitamin C is indispensable. Intense training increases oxidative stress and microinflammation — and Vitamin C is one of the body’s first lines of defense.
Supplementation and adequate intake have been shown to reduce muscle soreness, improve recovery, and support collagen regeneration in tendons and ligaments. Studies also suggest that Vitamin C may lower cortisol levels after strenuous exercise, contributing to better hormonal balance.
However, excess supplementation (above 1,000 mg/day) can blunt certain adaptive training responses, particularly mitochondrial adaptations to endurance training. For this reason, athletes should prioritize whole-food sources rather than megadoses in pill form.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the recommended daily intake is:
- Men: 90 mg per day
- Women: 75 mg per day
- Smokers: +35 mg per day (due to increased oxidative stress)
During illness, recovery, or intense training cycles, requirements can temporarily rise to 150–200 mg per day.
How to Reach the RDI Naturally
You can easily meet your daily Vitamin C needs through fresh, colorful foods:
- 1 medium orange (130 g) → ~70 mg
- ½ cup of raw red bell pepper → ~60 mg
- 1 kiwi fruit → ~60 mg
- 1 cup of strawberries → ~85 mg
- ½ cup of cooked broccoli → ~50 mg
Combining multiple sources throughout the day ensures consistent absorption, as Vitamin C is rapidly metabolized and excreted in urine.
Final Considerations
Vitamin C is not just an immune booster — it’s a biochemical multitool that strengthens tissues, accelerates recovery, and protects against oxidative stress.
For athletes, it bridges the gap between performance and resilience. It keeps the body’s engine running clean, minimizing the wear and tear caused by training and daily life. In essence, Vitamin C fuels not only the body’s defense but also its ability to rebuild stronger after every challenge.
In the pursuit of endurance and vitality, Vitamin C is the molecule of resilience.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.