Definition
Potassium is a major intracellular electrolyte that regulates fluid balance, nerve signaling, and muscle contraction. It works in concert with sodium to maintain cellular electrical gradients — the foundation of every heartbeat, thought, and movement.
This mineral is vital for maintaining blood pressure stability, hydration, and neuromuscular coordination. Because it operates inside cells, even small changes in potassium concentration can dramatically influence energy levels, cardiac rhythm, and muscular precision.
Where It’s Found
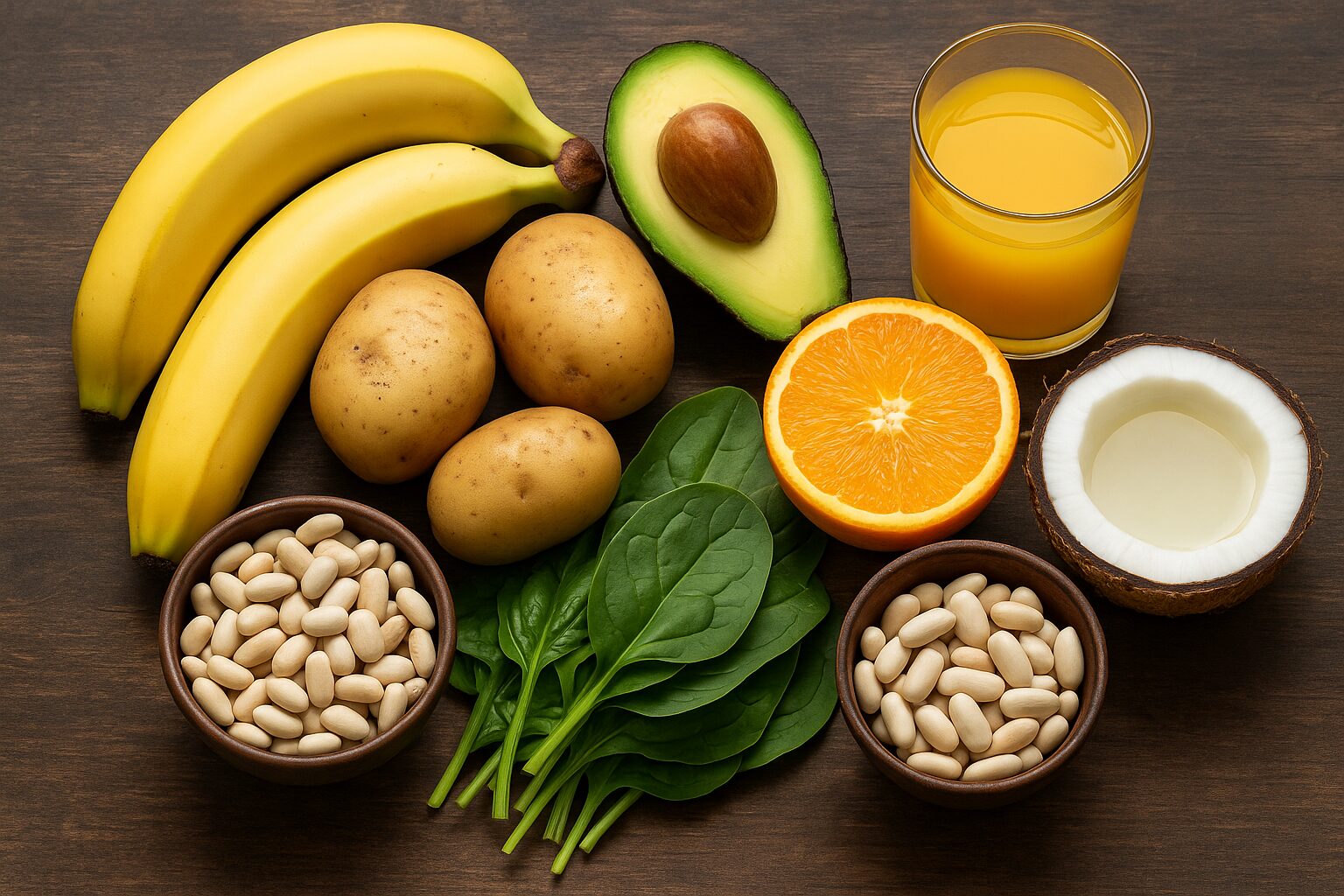
Potassium is abundant in whole, unprocessed foods, especially fruits, vegetables, legumes, and dairy products. Excellent sources include bananas, potatoes, avocados, spinach, oranges, yogurt, and beans.
Modern diets high in processed foods tend to be sodium-rich and potassium-poor, disrupting the natural electrolyte ratio that the human body evolved to maintain. Restoring this balance is crucial for cardiovascular and muscular health.
Function in the Human Body
Potassium’s most critical role is maintaining electrical neutrality across cell membranes. It allows nerves to transmit signals and muscles — including the heart — to contract properly. It also regulates acid-base balance, ensuring the body’s pH remains stable.
By pulling water into cells, potassium supports hydration at the cellular level, reducing fatigue and muscle cramping. It also works as a natural vasodilator, helping blood vessels relax, improving circulation, and lowering blood pressure.
Relationship with Physical Performance
For athletes, potassium is one of the most performance-critical minerals. During exercise, it is lost through sweat, and even slight depletion can cause weakness, cramps, arrhythmias, and premature fatigue. Maintaining optimal levels enhances endurance, reaction time, and recovery.
Potassium helps muscles store glycogen efficiently, which is crucial for sustained energy output. It also modulates nerve-muscle communication, making contractions smoother and more coordinated. After training, potassium replenishment restores electrolyte equilibrium and prevents delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS).
In endurance and combat sports — where dehydration and high-intensity intervals coincide — potassium intake can determine whether the athlete finishes strong or collapses early.
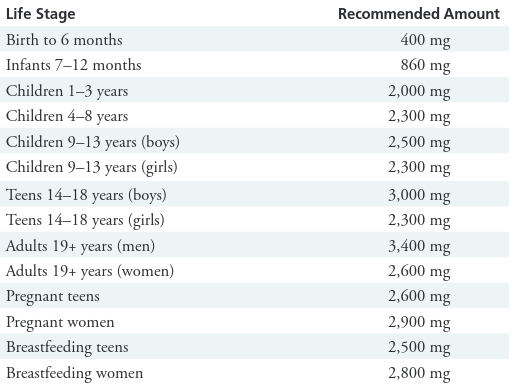
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
According to the National Academies of Sciences (NASEM):
- Men: 3,400 mg per day
- Women: 2,600 mg per day
Most adults consume less than 60% of the RDI due to insufficient fruit and vegetable intake. Unlike sodium, excess potassium from natural foods rarely poses a risk, as kidneys efficiently excrete the surplus in healthy individuals.
How to Reach the RDI Naturally
Potassium is easily obtained through a balanced diet of whole foods:
- 1 medium baked potato (with skin) → ~900 mg
- 1 avocado → ~700 mg
- 1 banana → ~420 mg
- 1 cup of cooked spinach → ~800 mg
- 1 cup of white beans → ~1,000 mg
- 1 cup of orange juice or coconut water → ~500 mg
Combining multiple sources throughout the day ensures steady electrolyte balance and optimal muscle function.
Final Considerations
Potassium is the electric heartbeat of human performance — governing every pulse, contraction, and recovery phase. It determines how well muscles contract, how quickly fatigue sets in, and how efficiently the body rehydrates.
While sodium drives short-term nerve firing, potassium maintains the rhythm of endurance, the calm after the storm, and the balance that prevents burnout.
In modern sports nutrition, it’s not just about fueling the body — it’s about powering its circuits. And in that regard, potassium is the current that keeps the athlete alive and performing at their peak.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.