Definition
Zinc is a trace mineral required for more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the human body. It regulates gene expression, supports immune defense, aids tissue repair, and contributes to hormone balance. Despite its small quantity in the body, zinc’s influence is vast — impacting growth, reproduction, taste perception, and even mental clarity.
Unlike some minerals, zinc is not stored in significant amounts, meaning a consistent daily intake is essential. Its role as a biochemical “catalyst” makes it indispensable for maintaining cellular efficiency and vitality.
Where It’s Found
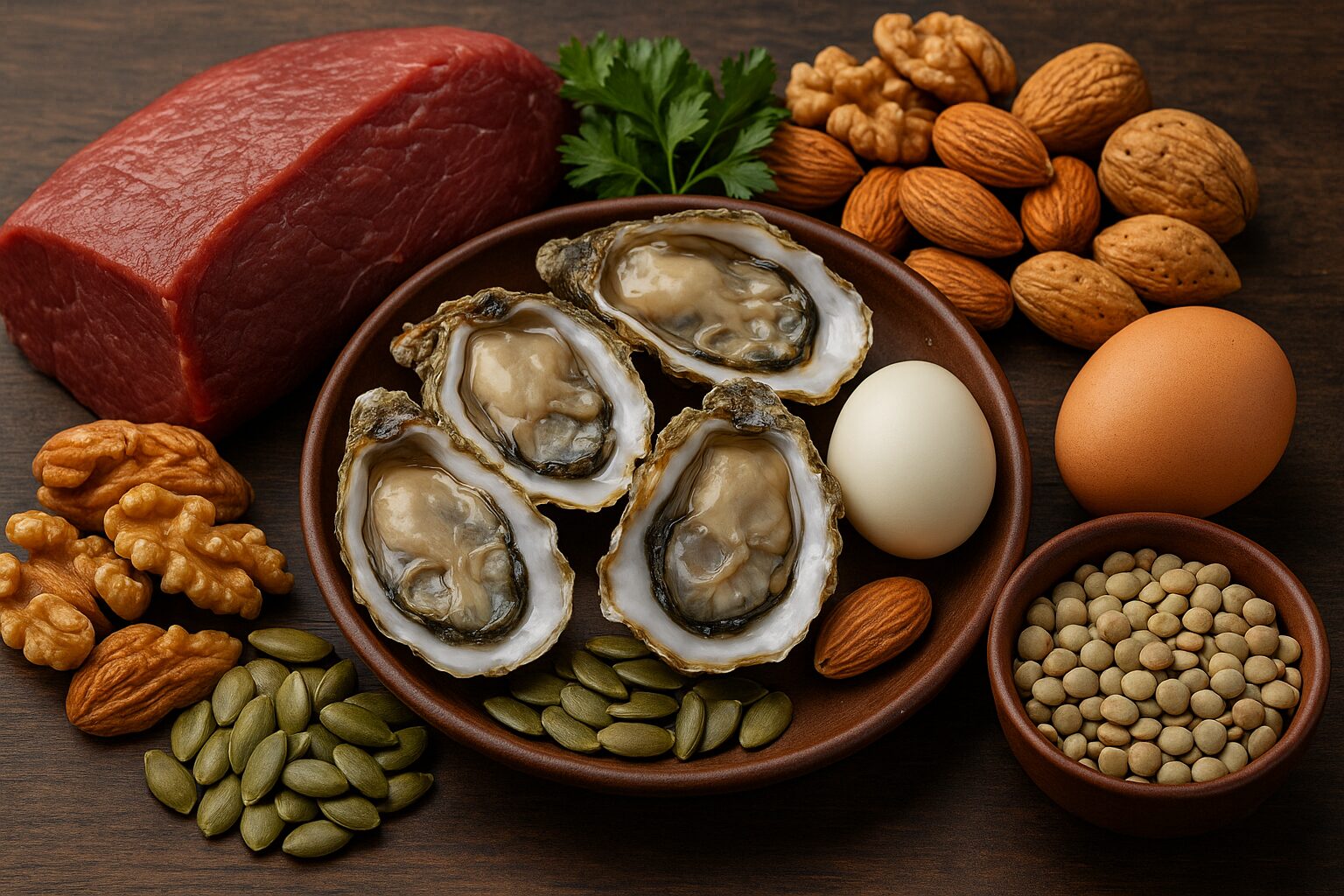
The richest sources of zinc come from animal proteins, particularly red meat, shellfish (especially oysters), poultry, and eggs. Plant-based sources like legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains also contain zinc, but with lower bioavailability due to the presence of phytates, which bind minerals and hinder absorption.
For vegetarians or vegans, soaking, fermenting, or sprouting plant foods can improve zinc absorption. Seafood and meat, however, remain the most efficient and concentrated natural sources.
Function in the Human Body
Zinc is often called the “repair mineral” because of its role in cell division, protein synthesis, and wound healing. It is critical for the production of enzymes that build and rebuild tissues, making it vital for recovery after physical exertion.
It also regulates testosterone production and insulin activity, influences taste and smell, and supports DNA and RNA synthesis — processes fundamental for cellular regeneration.
In the immune system, zinc enhances the activity of white blood cells and modulates inflammation, helping the body resist infection and recover faster from illness or injury.
Relationship with Physical Performance
Zinc directly affects athletic performance, muscle growth, and hormonal balance. Adequate zinc levels are linked to higher testosterone, faster recovery, and stronger immune function — all key factors in consistent training outcomes.
Deficiency, on the other hand, leads to decreased muscle repair, lower endurance, reduced strength, and greater susceptibility to illness. Chronic low zinc levels can suppress appetite, delay recovery from workouts, and impair sleep — a trifecta of setbacks for any athlete.
Supplementation can be beneficial in cases of deficiency, but excessive intake (>40 mg/day) can interfere with copper absorption and disrupt the delicate mineral balance that supports peak performance.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
- Men: 11 mg per day
- Women: 8 mg per day
- Pregnant women: 11–12 mg per day
Athletes, due to higher turnover and losses through sweat, may benefit from slightly higher intakes — ideally achieved through diet first, then supplementation if needed.
How to Reach the RDI Naturally
It’s easy to meet daily zinc needs through whole foods:
- 100 g of oysters → 60–80 mg (extremely rich)
- 100 g of beef or lamb → 5–6 mg
- 1 cup of cooked lentils → 2.5 mg
- 30 g of pumpkin seeds → 2.2 mg
- 1 egg → 0.6 mg
Pairing plant-based zinc sources with acidic foods (like lemon or tomato) can boost absorption by reducing phytate activity.
Final Considerations
Zinc is the silent force behind strength and resilience — the mineral that keeps the body’s repair systems, hormones, and immunity operating in perfect synchrony.
For athletes, it’s not just a nutritional detail; it’s a cornerstone of recovery, performance, and longevity. Whether you’re lifting, running, or simply trying to thrive under stress, zinc ensures your body remains in balance, capable of adapting and rebuilding stronger each day.
In essence, zinc fuels the biological craftsmanship of the human machine.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.