Definition
Sodium is a vital electrolyte that regulates fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction. Despite its controversial reputation, sodium is indispensable for maintaining blood pressure, nutrient transport, and cellular function.
It is the body’s main extracellular cation, working in harmony with potassium to sustain electrical gradients across cell membranes — the foundation of every heartbeat, nerve impulse, and muscular movement. Without sodium, hydration, performance, and life itself would cease.
Where It’s Found
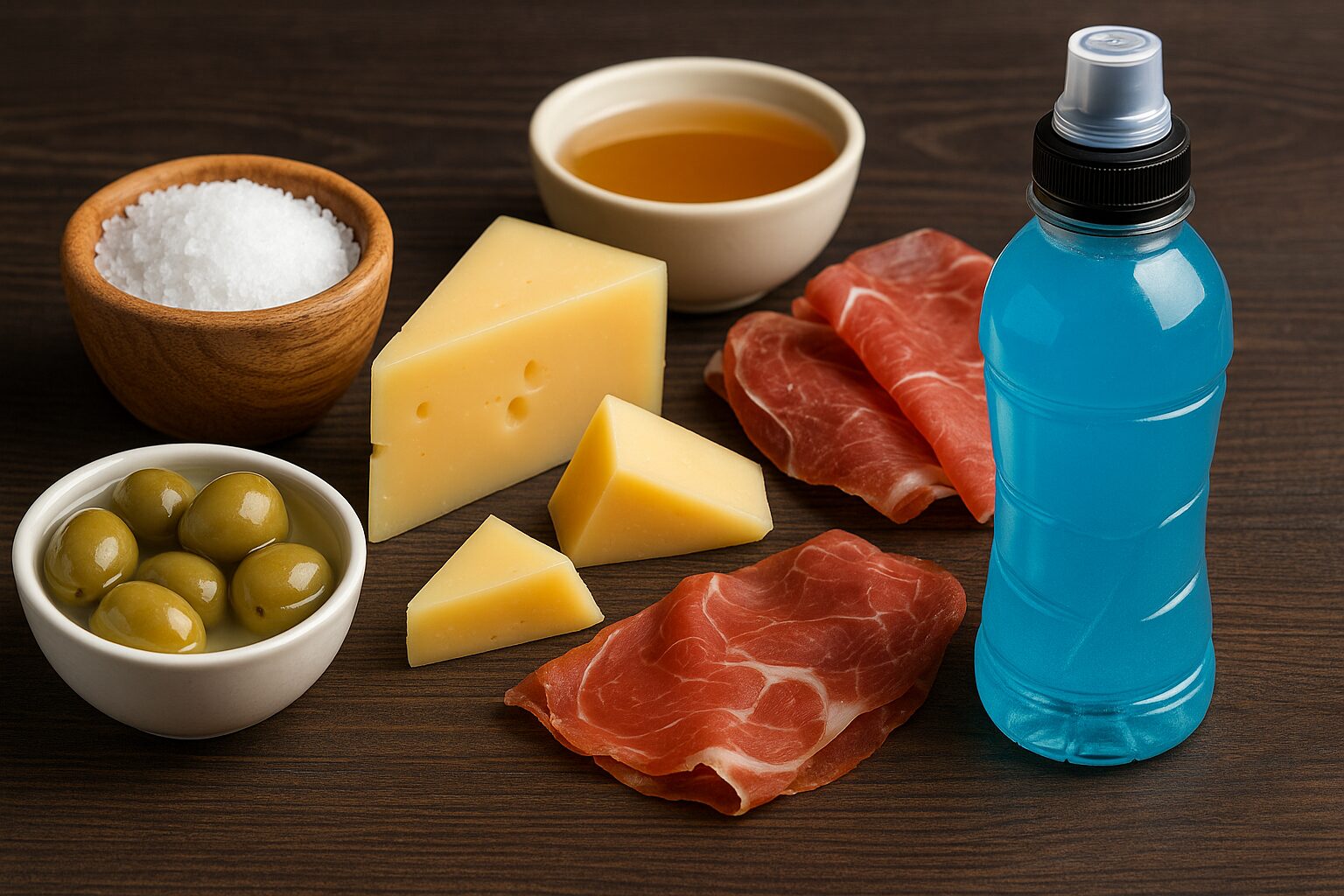
Sodium is naturally present in most foods and commonly consumed as sodium chloride (table salt). Major sources include sea salt, processed foods, soups, cheeses, olives, and cured meats.
However, the context matters: sodium from whole foods and hydration formulas plays a very different role from excessive sodium hidden in processed snacks. Athletes, in particular, often need more sodium than sedentary individuals due to sweat losses during training.
Function in the Human Body
Sodium controls the movement of fluids between compartments — ensuring that cells remain properly hydrated. It also allows the nervous system to transmit electrical signals and the muscular system to contract efficiently.
Furthermore, sodium influences acid-base balance, helping maintain optimal pH levels in the blood. It also regulates blood volume and pressure, ensuring adequate oxygen delivery during exercise or stress.
At the cellular level, sodium’s partnership with potassium (the sodium-potassium pump) is the electrical foundation of metabolism — a continuous exchange that keeps muscles firing and neurons active.
Relationship with Physical Performance
For athletes, sodium is a performance-critical nutrient. During prolonged or intense exercise, sodium is lost through sweat at rates ranging from 400 mg to over 2,000 mg per hour, depending on temperature, genetics, and intensity.
When sodium levels drop too low — a condition known as hyponatremia — symptoms such as cramps, dizziness, confusion, and even collapse can occur. Proper sodium intake ensures fluid retention, stable blood pressure, and optimal muscle contraction during endurance or heat exposure.
Contrary to the low-salt dogma, research now shows that athletes and physically active individuals may require significantly more sodium than the general population, particularly in hot climates.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
According to the National Academies of Sciences (NASEM):
- Adults (19–50 years): 1,500 mg/day (adequate intake)
- Upper limit: 2,300 mg/day for general population
- Athletes: 3,000–6,000 mg/day (depending on sweat loss and training volume)
For most healthy individuals, sodium excretion adapts to intake — meaning moderate increases in salt consumption do not automatically raise blood pressure when balanced with potassium and hydration.
How to Reach the RDI Naturally
Sodium is easy to obtain through both natural and added sources:
- ¼ teaspoon of table salt → ~575 mg
- 1 pickle or small portion of olives → ~400 mg
- 1 cup of chicken broth → ~800 mg
- 1 ounce of cheese → ~175 mg
- Sports drinks or electrolyte powders → 300–1,000 mg per serving
For endurance athletes, combining water, sodium, and potassium helps maintain plasma volume and prevents cramps during prolonged training or competition.
Final Considerations
Sodium is not the enemy — imbalance is. In the right amount, it fuels endurance, stabilizes nerves, and sustains hydration far more effectively than water alone.
Modern anti-salt narratives often overlook context: for athletes, laborers, and anyone under high physical demand, sodium is a performance enhancer, not a liability.
It’s not just about salt — it’s about precision. The right sodium intake keeps the body’s electrical system charged, hydrated, and ready for peak output.
In short: sodium powers your voltage.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.