Definition
Selenium is a trace mineral essential for antioxidant defense, thyroid function, and immune health. It acts primarily through selenoproteins, a unique class of enzymes that protect cells from oxidative damage, regulate metabolism, and modulate inflammation.
Although required only in microgram amounts, selenium’s impact is profound — influencing everything from fertility to muscle recovery and disease prevention. Its balance is delicate: both deficiency and excess can have harmful effects on cellular integrity and performance.
Where It’s Found
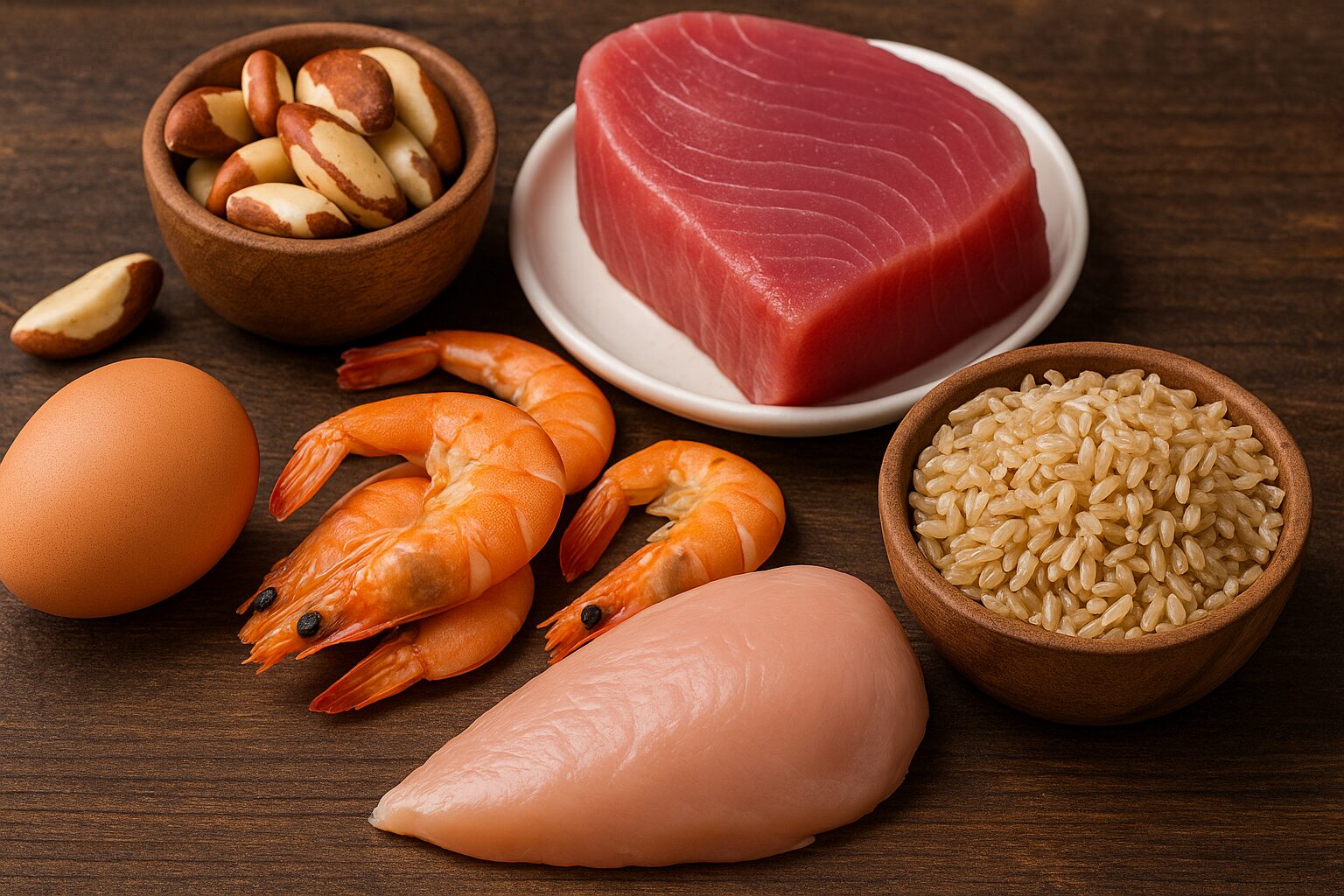
Selenium concentrations in food vary depending on soil content, making geographic location a key factor. The richest dietary sources are Brazil nuts, seafood (tuna, sardines, shrimp), eggs, meat, and whole grains.
Just one or two Brazil nuts can provide more than 100% of the daily recommended intake, making them one of the most potent natural sources on Earth. Plant-based foods like lentils and brown rice contain selenium as well, but levels depend heavily on the soil in which they were grown.
Function in the Human Body
Selenium is central to the body’s antioxidant defense system. It forms part of glutathione peroxidase (GPx), an enzyme that neutralizes free radicals and prevents lipid oxidation — protecting cell membranes from damage.
It also regulates thyroid hormone metabolism by converting inactive T4 into the active T3 form, directly linking selenium to energy production, temperature regulation, and weight control.
Furthermore, selenium modulates the immune response by supporting white blood cell function and reducing chronic inflammation, contributing to overall resilience and recovery.
Relationship with Physical Performance
For athletes and physically active individuals, selenium supports endurance, recovery, and hormonal balance. Exercise increases oxidative stress — and selenium helps counteract this by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated during intense training.
It also enhances testosterone production and thyroid function, both of which influence energy, muscle growth, and metabolic rate. Low selenium levels have been associated with increased fatigue, slower recovery, and higher risk of overtraining-related inflammation.
Because selenium works synergistically with Vitamin E, maintaining adequate levels of both is essential for optimal antioxidant protection and cellular repair.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
- Men and Women (Adults): 55 µg per day
- Pregnant Women: 60 µg per day
- Lactating Women: 70 µg per day
The upper limit is 400 µg per day. Chronic excessive intake (usually from supplements or too many Brazil nuts) can cause selenosis, characterized by hair loss, brittle nails, and digestive distress.
How to Reach the RDI Naturally
It’s remarkably easy to hit selenium targets with the right foods:
- 1 Brazil nut → 50–100 µg
- 100 g of tuna or sardines → 60–90 µg
- 2 eggs → ~30 µg
- 100 g of chicken or beef → ~25 µg
- 1 cup of brown rice or lentils → ~20 µg
Including just one or two selenium-rich foods daily provides all the protection your body needs without supplementation.
Final Considerations
Selenium is the body’s biochemical shield — a mineral that stands at the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and performance. It protects against oxidative damage, fine-tunes hormonal activity, and accelerates recovery after stress.
Its power lies in balance: too little weakens your defenses; too much overwhelms them. When paired with Vitamin E and a nutrient-dense diet, selenium amplifies resilience — both cellular and systemic.
In the hierarchy of micronutrients, selenium may be small in quantity, but it is mighty in consequence — the trace element that keeps your internal engine clean, efficient, and unstoppable.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.