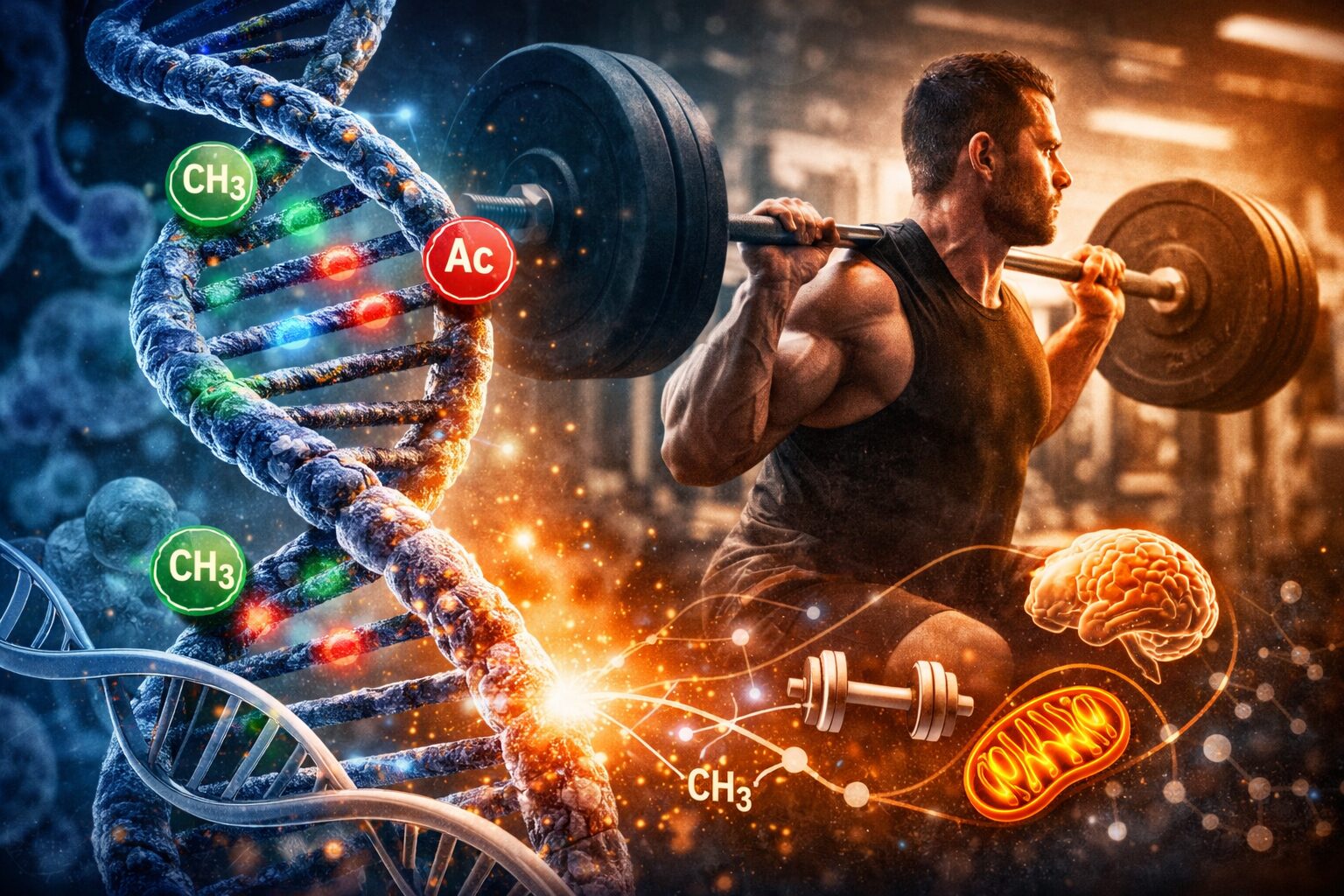
Epigenetics refers to biological mechanisms that regulate gene expression without changing your DNA sequence.
Your genetic code is fixed — but epigenetic marks determine how actively each gene is used.
The three major epigenetic mechanisms are:
- DNA methylation – chemical tags added to DNA that reduce gene expression.
- Histone modification – changes to the proteins around which DNA is wrapped, making genes more or less accessible.
- Non-coding RNAs – molecules that influence how genes are translated into proteins.
Think of your DNA as a piano.
Epigenetics is the pianist — determining which keys are played, how often, and how loudly.
The Role of Epigenetics in Physical Training
Training doesn’t just activate muscles — it activates genes.
Hundreds of studies now show that exercise produces powerful epigenetic changes, affecting:
1. Muscle Growth (Hypertrophy)
Resistance training alters DNA methylation patterns in skeletal muscle, increasing the activity of genes related to:
- protein synthesis
- satellite cell activation
- muscle fiber repair and growth
- mTOR signaling pathways
Research shows that after a single workout, over 7,000 genes in muscle tissue show epigenetic modifications that enhance long-term adaptation.
2. Strength Development
Strength gains depend on neural efficiency as much as muscle mass.
Epigenetic changes influence:
- motor-unit recruitment
- neuromuscular coordination
- myelination of motor pathways
Consistent training enhances expression of genes involved in neural plasticity — helping you learn movement patterns faster.
3. Fat Loss and Metabolism
Aerobic and anaerobic exercise modify epigenetic marks in genes associated with:
- fat oxidation
- insulin sensitivity
- mitochondrial biogenesis
- inflammation control
These changes help create a “metabolic memory” that makes fat loss and performance improvements easier over time.
4. Recovery and Injury Prevention
Epigenetic regulation influences collagen synthesis, inflammation, and tissue repair.
People with better recovery habits (sleep, protein intake, stress control) show more favorable epigenetic profiles.
Lifestyle directly shapes these biological responses.
Why Two People Training the Same Way Get Different Results
Epigenetics explains why training programs must be individualized.
Factors such as:
- sleep quality
- stress levels
- nutrition
- past training history
- environmental toxins
- age
- even psychological state
…can change how responsive your genes are to training stimuli.
This is why “copying your friend’s workout” rarely produces the same outcome.
Your biology is dynamic — and so must be your training approach.
How You Can Use Epigenetics to Improve Your Training
You can influence your epigenetic switches daily. Evidence-based ways include:
1. Train Regularly
Consistency strengthens positive epigenetic patterns.
Muscles retain an “epigenetic memory” of training that accelerates future gains.
2. Eat Protein and Nutrient-Dense Foods
Amino acids, vitamins (especially B vitamins), and minerals are required for epigenetic modification and DNA repair.
3. Sleep 7–9 Hours
Sleep deprivation disrupts epigenetic regulation of hormones, metabolism, and muscle recovery.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic cortisol exposure negatively alters methylation patterns related to muscle and fat metabolism.
5. Avoid a Sedentary Lifestyle
Even if you train daily, long periods of inactivity can reverse beneficial epigenetic effects.
6. Use Periodization
Changing training intensity and volume forces new patterns of gene expression — preventing plateaus.
Key Takeaway
Epigenetics shows that your body is not a fixed machine.
Your choices — training, nutrition, sleep, stress, environment — constantly control how your genes behave.
You are not limited by your genetics.
You are shaped by how you activate them.
When you understand epigenetics, you understand why smart programming, recovery, and lifestyle optimization are just as important as lifting weights.
And that’s exactly what transforms training from guesswork into science.
Forge Your Mind. Build Your Biology.
Join the Forge Biology newsletter — where science meets strength.
Every week, you’ll get:
-
Evidence-based insights on training, performance, and recovery
-
Real analyses of supplements that work (and the ones that don’t)
-
Deep dives into hormones, nutrition, and human optimization
No fluff. No marketing hype. Just data-driven knowledge to build a stronger body — and a sharper mind.
Subscribe now and start mastering your biology.